
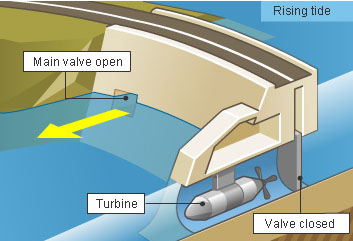
The salt water of the sea or ocean can easily corrode the blades of the turbine. And proper maintenance of this equipment under water may not be viable. Mechanical fluids such as lubricants can easily leak out, especially because of its use underwater and hence threaten the marine life. Some species of fish may no longer inhabitate the area if threatened by a constant moving or noise making apparatus or source. The rotating blades of the turbine can kill the swimming aquatic life forms.

The tidal power generating apparatus may have harmful effects on marine life.
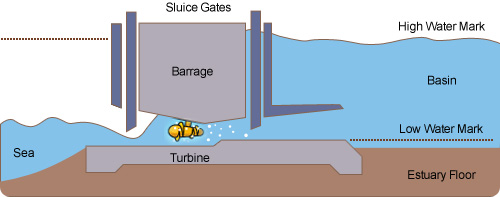

Rance tidal power plant – Dam of the tidal power plant on the estuary of the Rance River, Bretagne, France Dynamic tidal power: Dynamic tidal power is an untried but promising technology or method that uses both the potential as well as kinetic energy of the tides.They are among the oldest methods of tidal power generation, with the Rance tidal power plant in France using the same method. This is the key difference between a tidal barrage and a conventional dam. They first allow the water to move in during high tide and release the water back during low tide. They are dam like structures that capture the energy of water moving in and out of a bay. This energy can be seized with the placement of specialized dams on the course of flow. Tidal barrage: Tidal barrages make use of potential energy: that is the difference in height between the high and the low of the tides.They were first conceived in the 1970s during the oil crisis. Some tidal generators can be directly built into an existing bridge.
Tidal barrage generator#
Tidal stream generator (TSG): TSGs make use of the kinetic energy of the moving tides to rotate the turbines, in a similar way to wind turbines. Scientists and engineers are working on increasing the amount of electricity produced and also in making this form of energy more environment friendly and economically viable. Investors are not enthusiastic on investing in tidal power as there is no guarantee of good profits or benefitting the costumers. The Sihwa lake tidal power plant is the largest installation in the world with a capacity of 254MW. In fact only 20 sites in the world have been identified for possible tidal power stations. Tidal power generation is still in its infancy, as there are only a few commercial scale power plants in the whole world. It is used in areas where the difference between the rise and fall of the tides is large. Tidal energy is produced from the surge and fall of the ocean tides. Here, the water is captured in a pond or a catchment area and is allowed to strike a water wheel whose mechanical energy or power was used to mill grain. Historically, however, tidal mills have been used in Europe and America. Though not widely used now, it has a good potential for future electricity generation. It is a fairly new advancement in the area of renewable power generation, with the world’s first large tidal power plant being set up in the year 1966, under the name Rance Tidal Power station in France. Tunnels allowing the tides to go in and out as the water flows through. Tidal power is the only technology that draws energy inherent in the orbital characteristics of the Earth-moon system, and to a lesser extent in the Earth-sun system. Because the earth’s tides are ultimately due to the gravitational forces between the sun, the moon and the earth, tidal energy is practically inexhaustible thereby getting classified under renewable energy. A tide is created by the gravitational effect of the sun and the moon on earth, thereby causing cyclical movement of the seas, leading to the tides. Tidal energy, also known as tidal power is a renewable form of hydropower where the kinetic or potential energy of the tides are used for the generation of electricity.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
